Can gynecomastia go away with exercise? Yes, in some cases, exercise can help reduce the appearance of gynecomastia, especially if it’s caused by excess body fat. However, it won’t cure all types of gynecomastia, particularly those stemming from hormonal imbalances or glandular tissue growth.
Gynecomastia, often referred to as “man boobs,” is a common condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. This can be a source of significant self-consciousness and insecurity for many men. A frequent question that arises is whether lifestyle changes, specifically exercise, can reverse this condition. The answer, like many things related to the human body, is nuanced. While exercise is undeniably beneficial for overall health and can certainly improve the appearance of the chest, its effectiveness in eliminating gynecomastia depends on the underlying cause of the condition.
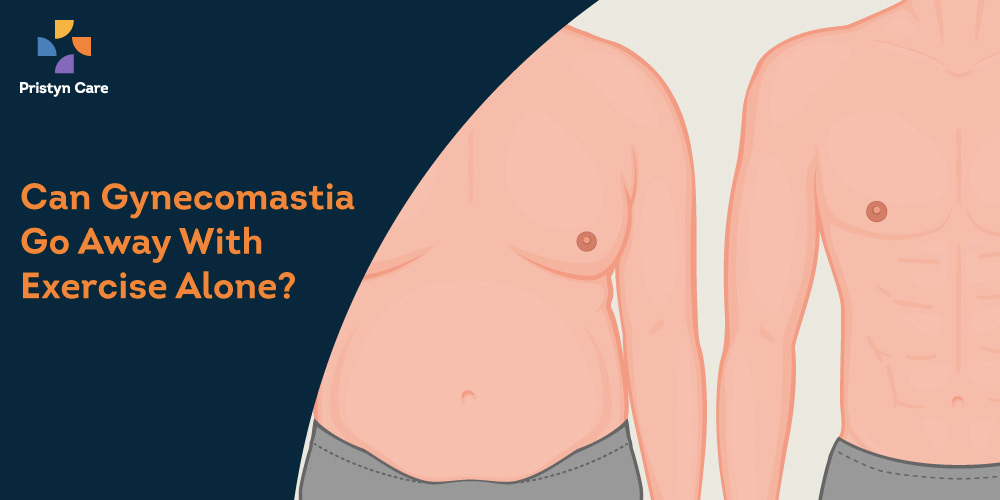
Image Source: www.pristyncare.com
Deciphering the Causes of Gynecomastia
To grasp whether exercise can help, we first need to comprehend the different reasons why men develop gynecomastia. It’s not just about having a bit of extra weight around the chest.
1. Physiological Gynecomastia: This is the most common form and occurs naturally during specific life stages.
* Newborns: Infants can experience temporary breast enlargement due to maternal hormones.
* Puberty: During puberty, hormonal fluctuations are common, leading to transient gynecomastia in many adolescent boys. This usually resolves on its own.
* Aging: As men age, testosterone levels can decline, and body fat may increase, potentially leading to hormonal imbalances that cause breast tissue growth.
2. Pathological Gynecomastia: This is caused by underlying medical conditions or external factors that disrupt the normal hormone balance.
* Hormonal Imbalances: A key factor in gynecomastia is an imbalance between estrogen (the primary female sex hormone) and testosterone (the primary male sex hormone). If estrogen levels are too high relative to testosterone, or if testosterone levels are too low, breast tissue can develop.
* Medications: Many prescription drugs can have gynecomastia as a side effect. These include certain heart medications, anti-ulcer drugs, cancer treatments, and even some anabolic steroids.
* Medical Conditions: Liver disease, kidney failure, thyroid problems, tumors of the testicles or adrenal glands, and HIV/AIDS can also contribute to gynecomastia.
* Substance Use: Excessive alcohol consumption, marijuana, heroin, and amphetamines have been linked to gynecomastia. The use of anabolic steroids is a significant culprit, as many steroids are converted into estrogen in the body, leading to estrogen dominance.
3. Pseudogynecomastia (Adipose Gynecomastia): This is not true gynecomastia but rather an accumulation of excess fat in the chest area, making the chest appear enlarged and to have a breast-like shape. This is often what people refer to when they talk about “man boobs” and is directly related to overall body fat percentage.
The Role of Exercise in Addressing Gynecomastia
Now, let’s delve into how exercise impacts these different types of gynecomastia.
Targeting Pseudogynecomastia (Adipose Gynecomastia)
If the enlarged chest appearance is due to excess fat, then exercise and diet become powerful tools. This is where chest fat reduction and achieving a lower body fat percentage are key.
- Calorie Deficit: The fundamental principle of fat loss is creating a calorie deficit, meaning you burn more calories than you consume. Exercise plays a crucial role in increasing your calorie expenditure.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Activities like running, swimming, cycling, and brisk walking are excellent for burning calories and improving cardiovascular health. Consistent cardio helps to systematically lower your overall body fat percentage, which will naturally reduce the fat deposits in your chest area.
- Strength Training: While cardio is king for fat burning, weight training for gynecomastia is essential for building muscle and improving body composition. Focusing on pectoral muscle definition can make the chest appear firmer and more sculpted, even if some fatty tissue remains.
How Exercise Contributes:
- Increased Metabolism: Building muscle through strength training boosts your resting metabolic rate, meaning you burn more calories even when you’re not exercising.
- Improved Body Composition: As you lose fat and gain muscle, your body composition improves. This leads to a leaner, more toned physique, which can significantly diminish the appearance of “man boobs.”
- Hormonal Benefits: Exercise, particularly resistance training, can positively influence hormone levels. It can help increase testosterone levels and improve insulin sensitivity, both of which are beneficial for overall health and may indirectly help with hormonal balance, though it’s not a direct cure for gynecomastia caused by severe hormonal imbalances.
Fat Loss Strategies: A combination of consistent cardio and a balanced diet is crucial. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities at least two days a week.
Can Exercise Help with True Gynecomastia?
When gynecomastia is caused by an overgrowth of glandular breast tissue, exercise alone cannot shrink this tissue. The enlarged tissue is not fat that can be burned off.
- Hormones and Exercise: While exercise can influence hormones and exercise such as testosterone, it’s unlikely to correct significant hormonal imbalances that are causing glandular tissue growth. Conditions like estrogen dominance, where estrogen levels are disproportionately high compared to testosterone, require medical intervention to address the root cause.
- Testosterone Levels: For men with low testosterone, exercise might help slightly increase levels, but it’s unlikely to be enough to reverse established glandular gynecomastia. Testosterone replacement therapy or other medical treatments are often necessary.
- Steroid Side Effects: If gynecomastia is a result of steroid side effects, particularly anabolic steroids that convert to estrogen, stopping the use of these substances is the first and most crucial step. Medical treatment may be required to manage the hormonal disruption.
- Estrogen Dominance: In cases of estrogen dominance, lifestyle changes like exercise and diet are supportive but usually insufficient on their own. A doctor would typically investigate the cause of the excess estrogen and recommend appropriate treatment, which might include medication to block estrogen’s effects or address the underlying condition.
What Exercise Can Do: Even if exercise doesn’t shrink the glandular tissue, it can still be beneficial:
- Build Pectoral Muscles: Weight training for gynecomastia can help build the pectoral muscles underneath the breast tissue. This can create a firmer, more defined chest appearance, making the gynecomastia less noticeable. Developing strong pectoral muscles can create a more athletic contour, helping to mask the appearance of enlarged breast tissue.
- Reduce Overall Body Fat: If you have both glandular gynecomastia and excess chest fat, exercising will help reduce the fat component, improving your overall chest appearance. This is a dual benefit: reducing fat and improving the tone of the underlying muscles.
Effective Exercise Regimens for Chest Appearance
When aiming to improve the appearance of the chest, especially when dealing with gynecomastia, a comprehensive approach combining cardio and targeted strength training is best.
Cardiovascular Exercise for Fat Loss
Cardio is paramount for lowering your overall body fat percentage, which is crucial if pseudogynecomastia is a factor.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods. This is highly effective for burning calories in a shorter amount of time and can boost metabolism post-workout.
- Examples: Sprints, burpees, jumping jacks, mountain climbers.
- Steady-State Cardio: Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise performed for a longer duration. This is excellent for sustained calorie burn and cardiovascular health.
- Examples: Jogging, cycling, swimming, brisk walking.
Frequency and Duration: Aim for at least 3-5 sessions per week, with each session lasting 30-60 minutes.
Weight Training for Gynecomastia: Targeting the Pectorals
While you can’t spot-reduce fat from the chest, you can build the pectoral muscles to create a more aesthetically pleasing and firmer chest. Remember, the goal here is pectoral muscle definition, not solely fat reduction from the chest itself.
Here are effective exercises and principles:
Key Principles:
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the weight, repetitions, or sets over time to continue challenging your muscles.
- Proper Form: Prioritize correct technique to maximize muscle engagement and prevent injuries.
- Full Range of Motion: Ensure you move the weight through its complete intended path to work the muscles effectively.
- Balanced Routine: Don’t neglect other muscle groups. A balanced physique contributes to a better overall appearance.
Effective Exercises:
1. Bench Press (Barbell or Dumbbell)
- Focus: Works the entire pectoral muscle, as well as triceps and shoulders.
- How-to: Lie on a bench, feet flat on the floor. Grip the barbell slightly wider than shoulder-width apart (or hold dumbbells). Lower the weight to your chest in a controlled manner, then press it back up.
- Sets and Reps: 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions.
2. Incline Bench Press (Barbell or Dumbbell)
- Focus: Targets the upper portion of the pectoral muscles, often contributing to a more lifted and sculpted look.
- How-to: Similar to the bench press, but performed on an inclined bench (15-30 degrees).
- Sets and Reps: 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions.
3. Dumbbell Flyes
- Focus: Isolates the chest muscles, promoting a wider stretch and contraction.
- How-to: Lie on a flat or inclined bench. Hold dumbbells above your chest with palms facing each other. Lower the dumbbells out to the sides in a wide arc, keeping a slight bend in your elbows, until you feel a stretch in your chest. Bring them back up to the starting position.
- Sets and Reps: 3-4 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
4. Push-Ups
- Focus: A versatile bodyweight exercise that engages the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Can be modified for difficulty.
- How-to: Start in a plank position, hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Lower your chest towards the floor, keeping your body in a straight line, then push back up.
- Variations: Kneeling push-ups (easier), decline push-ups (harder, targets upper chest).
- Sets and Reps: Aim for 3 sets to near failure.
5. Dips (Chest Version)
- Focus: Primarily targets the lower chest.
- How-to: Using parallel bars, grip the bars and lower your body by bending your elbows until your chest is about level with your hands. Lean forward slightly to emphasize the chest. Push back up to the starting position.
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of as many repetitions as possible (AMRAP).
6. Cable Crossovers
- Focus: Excellent for isolating the chest and achieving a good contraction, especially in the inner chest.
- How-to: Stand between two cable machines with pulleys set at chest height. Grab the handles and bring them together in front of your chest in an arc motion, squeezing your chest muscles.
- Sets and Reps: 3-4 sets of 12-15 repetitions.
Sample Weekly Workout Plan (Strength Training):
| Day | Focus | Exercises | Sets | Reps | Rest (sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Chest & Triceps | Barbell Bench Press, Incline Dumbbell Press, Dumbbell Flyes, Push-ups, Dips | 3-4 | 8-15 | 60-90 |
| Tuesday | Back & Biceps | Pull-ups, Rows, Bicep Curls | 3-4 | 8-12 | 60-90 |
| Wednesday | Rest or Cardio | Light cardio or complete rest | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Thursday | Shoulders & Legs | Overhead Press, Lateral Raises, Squats, Lunges | 3-4 | 8-12 | 60-90 |
| Friday | Chest & Abs | Cable Crossovers, Decline Push-ups, Plank variations | 3-4 | 12-15+ | 60-90 |
| Saturday | Full Body/Cardio | Moderate Cardio or light full-body circuit | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Sunday | Rest | Complete Rest | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Important Note: This is a sample. Adjust based on your fitness level and recovery.
Diet and Exercise for Man Boobs: A Holistic Approach
Effective management of gynecomastia, especially if it involves excess fat, requires a synergistic approach involving both diet and exercise for man boobs.
Dietary Recommendations:
- Calorie Control: To achieve chest fat reduction, a consistent calorie deficit is essential. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
- Lean Protein: Include sources like chicken breast, fish, lean beef, eggs, and legumes. Protein helps with satiety and muscle repair.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Opt for brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-wheat bread for sustained energy.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are good sources of healthy fats, which are important for hormone production.
- Fruits and Vegetables: These are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber, aiding digestion and overall health.
- Limit Processed Foods and Sugars: These contribute empty calories and can hinder fat loss.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Lifestyle Factors:
- Alcohol Consumption: Moderate alcohol intake, as excessive alcohol can disrupt hormone balance and contribute to fat gain.
- Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Poor sleep can negatively impact hormone levels, including testosterone.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which can promote fat storage, particularly around the abdomen.
When Exercise Isn’t Enough: Medical Consultation
It’s crucial to reiterate that exercise is most effective for gynecomastia caused by excess body fat (pseudogynecomastia). If you suspect your gynecomastia is due to glandular tissue growth or a hormonal imbalance, you must consult a medical professional.
When to See a Doctor:
- If gynecomastia appears suddenly.
- If it occurs in only one breast.
- If it is accompanied by breast pain or discharge.
- If you experience other symptoms like testicular pain or loss of libido.
- If the condition persists despite significant weight loss and consistent exercise.
A doctor can perform a physical examination, blood tests to check hormone levels, and potentially imaging studies to determine the cause. Treatment options may include:
- Medication: To help rebalance hormones.
- Surgery: For cases where glandular tissue is significantly enlarged and hasn’t responded to other treatments, surgical removal (mastectomy) might be an option. This is typically considered for true gynecomastia, not pseudogynecomastia.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can gynecomastia disappear completely with exercise?
A1: If the gynecomastia is due to excess body fat (pseudogynecomastia), then significant improvement and potentially a complete reduction in the appearance of “man boobs” can be achieved through a combination of diet and exercise. However, if it’s due to overgrown glandular breast tissue, exercise alone will not make it disappear.
Q2: Will weight training reduce breast fat?
A2: Weight training builds muscle, which increases your metabolism and helps burn calories. While it doesn’t directly burn fat from the chest area, it contributes to overall fat loss when combined with a calorie deficit, leading to a reduction in chest fat.
Q3: Are there specific exercises to get rid of gynecomastia?
A3: There are no specific exercises that target and eliminate glandular breast tissue. However, exercises that build pectoral muscles, like bench presses and push-ups, can improve the chest’s appearance and make gynecomastia less noticeable. Cardio exercises are crucial for overall fat loss.
Q4: How long does it take to see results from exercise and diet for gynecomastia?
A4: Results vary depending on the individual, the severity of the condition, and adherence to the diet and exercise plan. Significant changes can typically be seen within 2-3 months of consistent effort, but long-term commitment is key.
Q5: Can exercise increase testosterone levels to help with gynecomastia?
A5: Yes, regular exercise, particularly resistance training, can help increase testosterone levels. This might offer some benefit if low testosterone is a contributing factor to gynecomastia, but it’s unlikely to be sufficient to reverse glandular tissue growth on its own.
Q6: Is it possible to have both fat and glandular tissue contributing to my gynecomastia?
A6: Absolutely. It’s common for men to have both excess adipose tissue (fat) and some degree of glandular enlargement contributing to the appearance of enlarged breasts. In such cases, a combined approach of fat loss through diet and exercise, along with potential medical treatment for glandular tissue, would be most effective.
Q7: What are the risks of using anabolic steroids regarding gynecomastia?
A7: Anabolic steroids can significantly disrupt the body’s natural hormone balance. Many steroids convert to estrogen in the body, leading to a state of estrogen dominance. This is a common cause of steroid-induced gynecomastia, which can be severe and persistent, often requiring medical intervention.
In conclusion, while exercise is a powerful tool for improving overall health and body composition, its ability to directly eliminate gynecomastia is limited to cases where excess fat is the primary cause. For true glandular gynecomastia, a medical diagnosis and treatment plan are often necessary. However, incorporating a consistent exercise routine and a healthy diet will always contribute positively to your physique and well-being, potentially reducing the visibility of gynecomastia and improving self-confidence.